- Whole Genome Sequencing
- Whole Exome Sequencing
- Comprehensive Genomic Profiling
Next-Generation Sequencing
NGS Services
Gene on Link and KimForest Laboratories provide high-quality NGS testing services. Our scope of services covers a wide range of research areas, including cancer research, agriculture, aquaculture, and other basic research studies. We offer highly customized services, from sample pick-up to report generation, to meet our clients’ needs.
With a commitment to diversified thinking in the post-genomic era, we integrate talent from biology, bioinformatics, and statistics to develop core value-added data analysis services. By establishing a big data value-added trading platform, we offer a comprehensive suite of bioinformatics analysis services — from cutting-edge experimental design and innovative genetic testing to advanced bioinformatics techniques and customized data presentation and reporting.
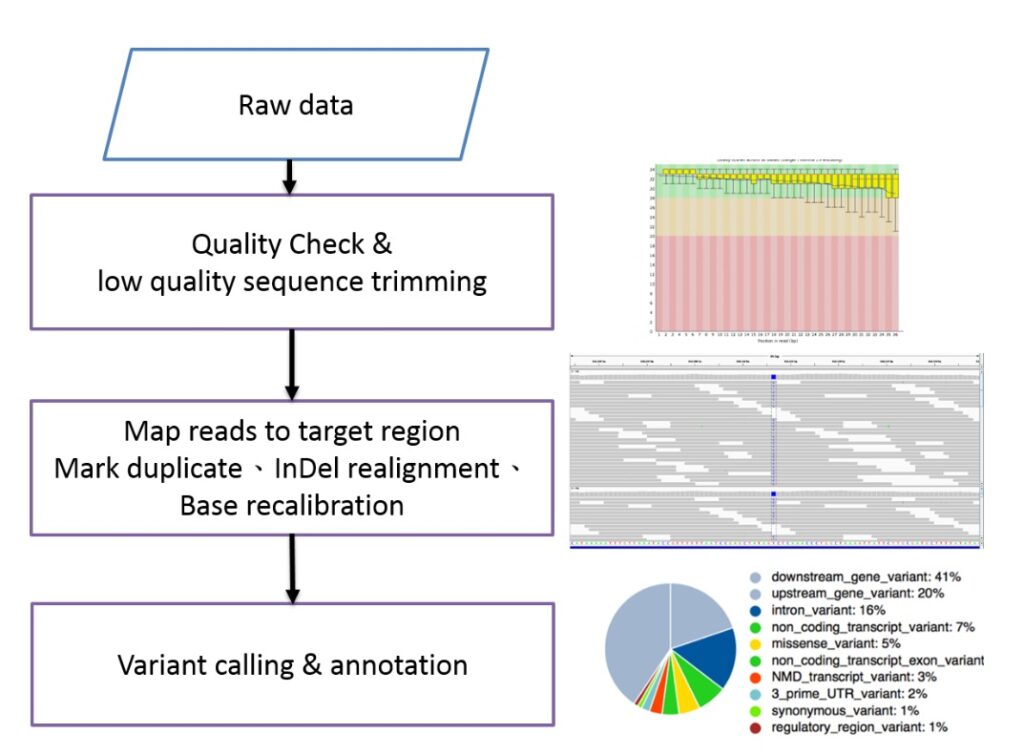
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) and Whole Exome Sequencing (WES)
Involve using next-generation sequencing (NGS) or third-generation sequencing technologies to obtain large volumes of short sequence fragments. When aligned with a reference genome, these fragments allow for the detection of genetic differences between the sequenced sample and the reference. These variations can then be analyzed to understand their impact on the organism, infer biochemical metabolic pathways, and study evolutionary relationships.
Comprehensive Genomic Profiling
This approach involves using a reference sequence to design primers that capture specific genome fragments or genes. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology is then used to obtain numerous short sequence fragments, which are aligned to the target regions in the reference genome. This enables the detection of differences between the sequenced sample and the reference within these areas. Compared to whole-genome sequencing, this method focuses on shorter regions, effectively reducing experimental costs. It also allows for high-coverage sequencing of targeted regions and the large-scale sequencing of thousands of samples for subsequent statistical analysis.
RNA-Sequencing
This method uses next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology to measure mRNA expression levels under specific conditions or to identify new isoforms. Unlike microarrays, RNA-Seq avoids issues of fluorescent signal saturation, providing a broader detection range. It also offers the potential to discover new isoforms, gene fusions, or single nucleotide variations. RNA-Seq can identify genes with differential expression across groups, and these differences can be analyzed to determine involvement in biochemical metabolic pathways, enabling a deeper understanding of how various conditions impact the organism.